Instability
Before surgery :

- The joint of the shoulder is one of the most mobile in the human body thanks to the thin interlocking of its two joint pieces, the humeral head which is one third of a sphere shape ( a tennis ball) and the shoulder blade glenoid cavity which is small and flat ( like a 2 euro coin). In return, this mobility results in a great potential for instability.
- Shoulder dislocation is frequent, it corresponds to a contact loss between the humeral head and shoulder blade glenoid cavity (= »displacement ». Its origin is traumatic more often than not and due to anterior slip out of the socket (the humeral head slips forward).
- Sport activities are often the source of dislocation events. All sports are concerned but sports with « wind up, early cocking throws » such as handball or volleyball and contact sports like rugby, football or judo can cause numerous accidents.
- Dislocation events cause damage to the ligaments ensuring joint stability, most often at the level of their insertion into the glenoid cavity (Bankart lesion) as well as bone injuries when the humeral head has impacted the anterior glenoid.
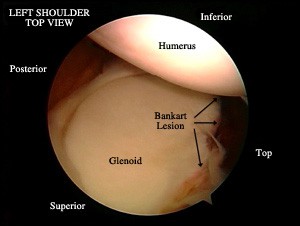
- Immobilization after a dislocation is mandatory; its duration depends on the number of previous dislocations. It can last for 4 weeks at a minimum for a first injury. Despite immobilization injuries do not heal easily and are subject to recurrence all the more so as the patient is young and practicing risk sports.
- A dislocation that heals by itself or is incomplete is known as a subluxation.
- For the surgeon to opt with his patient for stabilization surgery it is necessary to have a trauma record documented with dislocations or subluxations and a feeling of apprehension known as (« dislocation fear ») in daily life or during sport activities causing discomfort.
During surgery :
There are two major types of stabilization surgery :
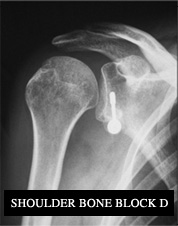
- The Bristow-Latarjet bone block or coracoid bone block procedure consists in shifting a bone piece to which powerful muscles remain attached onto the lower part of the glenoid anterior face. It allows to create a real wall in front of the humeral head to prevent dislocations.
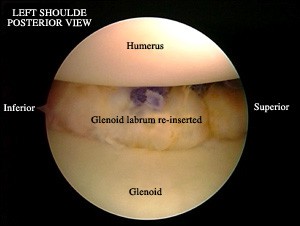
- The Bankart procedure involves re-attaching and re-inserting the labrum and ligaments torn during the dislocation with small anchors and sutures into the glenoid. This procedure is currently performed arthroscopically with 2 or 3 one centimeter incisions and without any muscular section.
- Choosing a type of procedure depends on the age of the patient, on the clinical examination data and the damage extant in the shoulder region.
After surgery :
- The mean duration of hospitalization is from 24 to 48H
- After surgery the shoulder is immobilized in a sling keeping the arm against the thorax and the elbow folded. The immobilization will last 4 weeks.
- The shoulder rehabilitation begins from the day after surgery and should be continued for several months according to a specific protocol in keeping with the performed procedure.
- Resuming high risk sport activities is allowed from between the 4 th and the 6 th post-op months. With sportspeople this is preceded by a specific rehabilitation therapy for physical preparation in order to guarantee maximum safety.
Latest breakthroughs :
- The clinical results analysis of arthroscopic stabilizations has allowed to better define and specify the indications of such repairs. Therefore, the instability recurrence rate tends to get near the coracoid bone block stabilizations (around 5%).
- Today the development of arthroscopic techniques makes it possible to associate the elective treatment of some lesions which could not be treated until then to the repair of the glenoid labrum.